MANGLA DAM: LOCATION, BENEFITS, AND POWER GENERATION

Introduction
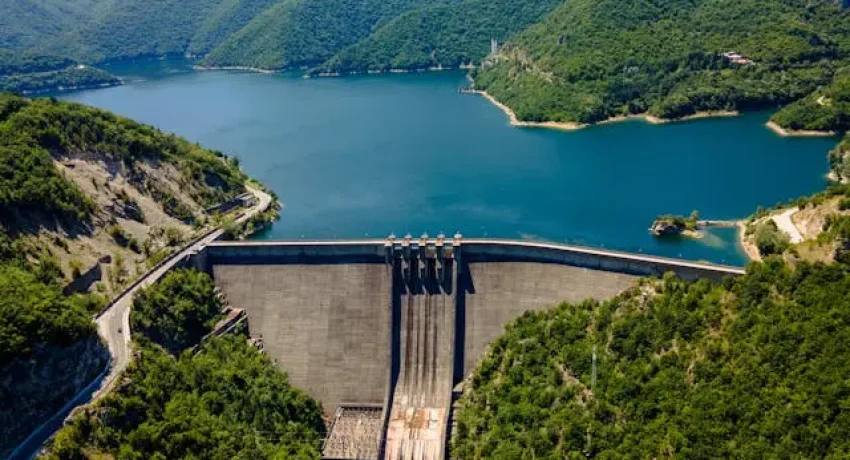
Mangla Dam is an integral part of Pakistan’s water management and energy infrastructure, serving as a major source of hydroelectric power and irrigation water. Located in Azad Jammu and Kashmir, this iconic structure stands as one of the largest dams in the country. From agricultural benefits to electricity production, Mangla Dam plays a pivotal role in the country’s economic stability and environmental sustainability. This article will delve into its location, geographical features, benefits, role in power generation, and its overall significance.
Mangla Dam: A Vital Asset for Pakistan’s Water and Energy Needs
1. Location of Mangla Dam
Mangla Dam is situated on the Jhelum River in the Mirpur District of Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan. The dam is located approximately 125 kilometers from Islamabad, the capital of Pakistan, making it easily accessible from major urban centers in the region. The dam’s strategic location in northeastern Pakistan places it at the intersection of key geographical and infrastructural zones, making it a cornerstone for regional development.
Mangla Dam creates a large reservoir known as Mangla Lake, which spans approximately 100 square kilometers. This lake serves as a vital water storage resource, used for irrigation, flood control, and water supply purposes. The Jhelum River, which flows through the dam, is one of the most significant tributaries of the Indus River, making this region crucial for the management of Pakistan’s water resources.
2. Geography of Mangla Dam and Its Surroundings
Mangla Dam is situated in a mountainous region, with a combination of hilly terrain and fertile plains surrounding the area. The geographical location of the dam has been carefully selected to take advantage of the natural topography, ensuring its ability to store and regulate water efficiently.
The dam itself is built within a valley, and its reservoir, Mangla Lake, is surrounded by hills and lush vegetation. The natural landscape enhances the aesthetic appeal of the area, while also contributing to the ecological balance of the region. Mangla Lake serves as an ecological haven for various species of birds, fish, and other wildlife, supporting biodiversity in the region.
The elevation of the area is also notable. The dam sits at an altitude of approximately 1,230 feet (375 meters) above sea level, while the water level in the reservoir reaches up to 1,237 feet (377 meters) during normal operation. The positioning of the dam at this altitude allows for the efficient generation of hydroelectric power, as it harnesses the energy from water flowing from a higher elevation to a lower one.
3. Historical Background and Construction of Mangla Dam
The construction of Mangla Dam was initiated in the 1960s as part of a broader water management strategy, which also included the development of the Tarbela Dam. The purpose of Mangla Dam was twofold: to provide a regulated supply of water for irrigation and to generate hydroelectric power. Its construction was part of Pakistan’s efforts to control water resources following the Indus Waters Treaty signed with India in 1960.
Construction began in 1961, with the dam being completed in 1967. However, the full operation of the dam wasn’t achieved until 1974. At the time of its completion, Mangla Dam was the largest earth-filled dam in the world, and it continues to be a major landmark in Pakistan’s history of large-scale infrastructure projects.
The dam was initially constructed with the primary aim of managing the waters of the Jhelum River and meeting the irrigation needs of the agricultural lands in Punjab. Over time, it has become even more important due to its role in hydroelectric power production and flood control.
4. Specifications of Mangla Dam
Mangla Dam is an earth-filled dam, constructed using layers of clay, gravel, and rock, which gives it the stability needed to hold back large volumes of water. The dam’s structural design allows it to withstand considerable pressures from both the water stored in its reservoir and external forces such as floods or seismic activity.
Key specifications of Mangla Dam include:
- Height: 147 meters (482 feet)
- Length: 3,140 meters (10,302 feet)
- Storage Capacity: 7.3 million acre-feet (MAF) of water
- Reservoir Area: 100 square kilometers (38.6 square miles)
These features make Mangla Dam one of the largest and most impressive dams in Pakistan, providing significant benefits for the country’s water and energy infrastructure.
5. Sea Level Elevation and Water Storage Capacity
The elevation of Mangla Dam plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of its functions, particularly in terms of water storage and power generation. The dam sits at an elevation of about 1,230 feet (375 meters) above sea level. This position ensures that the dam can store and regulate large quantities of water efficiently.
The storage capacity of the reservoir is approximately 7.3 million acre-feet of water, which is used to supply irrigation to over 2 million acres of agricultural land in Pakistan. The large volume of water stored in the reservoir also helps regulate the flow of water to avoid flooding in downstream areas during the monsoon season.
6. Benefits of Mangla Dam
a. Irrigation and Agriculture
Mangla Dam is vital for the agricultural sector in Pakistan, especially in the Punjab region. The controlled release of water from the reservoir feeds into the canal irrigation systems, providing water to millions of acres of farmland. This makes Mangla Dam a key asset for Pakistan’s food security, ensuring that the agricultural industry has access to reliable water supplies year-round.
Irrigation from Mangla Dam has significantly improved crop yields and enabled the cultivation of a variety of crops, including wheat, rice, cotton, and sugarcane. The consistent water supply helps stabilize agricultural production, benefiting farmers and boosting the national economy.
b. Power Generation
The Mangla Dam is also a crucial source of hydroelectric power generation. The dam’s power station is equipped with turbines that generate electricity by harnessing the energy from the water flowing through the dam. The initial power generation capacity was 1,000 MW, but upgrades over the years have increased this capacity to around 1,150 MW.
Hydropower from Mangla Dam contributes significantly to Pakistan’s national grid, supplying electricity to the northern and central regions of the country. The renewable energy produced is an essential part of Pakistan’s energy mix, helping to meet the growing demand for electricity while reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
c. Flood Control and Water Supply
Mangla Dam plays a critical role in flood control, especially during the monsoon season when heavy rains can lead to flooding in downstream areas. The dam’s reservoir helps regulate water flow by storing excess water during periods of high rainfall and releasing it gradually to prevent downstream flooding.
In addition to flood control, the dam provides water for domestic consumption and industrial use in the surrounding regions. It ensures a stable supply of water for both urban and rural populations, making it essential for the region’s overall water security.
d. Environmental and Ecological Benefits
Mangla Dam and its surrounding reservoir, Mangla Lake, offer numerous ecological benefits. The lake serves as a habitat for a variety of wildlife, including migratory birds and fish species. The region has become an important spot for birdwatching and ecotourism, further contributing to local tourism industries.
7. Electricity Production and Its Impact on Pakistan’s Energy Sector
Mangla Dam’s hydroelectric power generation capabilities have been a significant contributor to Pakistan’s electricity needs. The dam has not only provided a clean, renewable source of energy but has also helped stabilize the national grid by supplying a consistent and predictable flow of electricity.
Hydropower is a vital part of Pakistan’s renewable energy strategy, and Mangla Dam continues to be one of the largest contributors to the country’s renewable energy capacity. This contributes to reducing the carbon footprint of Pakistan’s energy sector and offers a sustainable solution to meet energy demands.
8. Challenges and Future Upgrades
While Mangla Dam continues to provide significant benefits, it faces challenges, including sedimentation in the reservoir, which reduces storage capacity over time. Furthermore, the impacts of climate change on water availability could pose a threat to the dam’s efficiency.
To address these challenges, the government of Pakistan has undertaken several upgrades, including the Mangla Dam Raising Project, which was completed in 2019. This project raised the height of the dam by 30 feet, allowing for increased water storage and enhanced power generation.
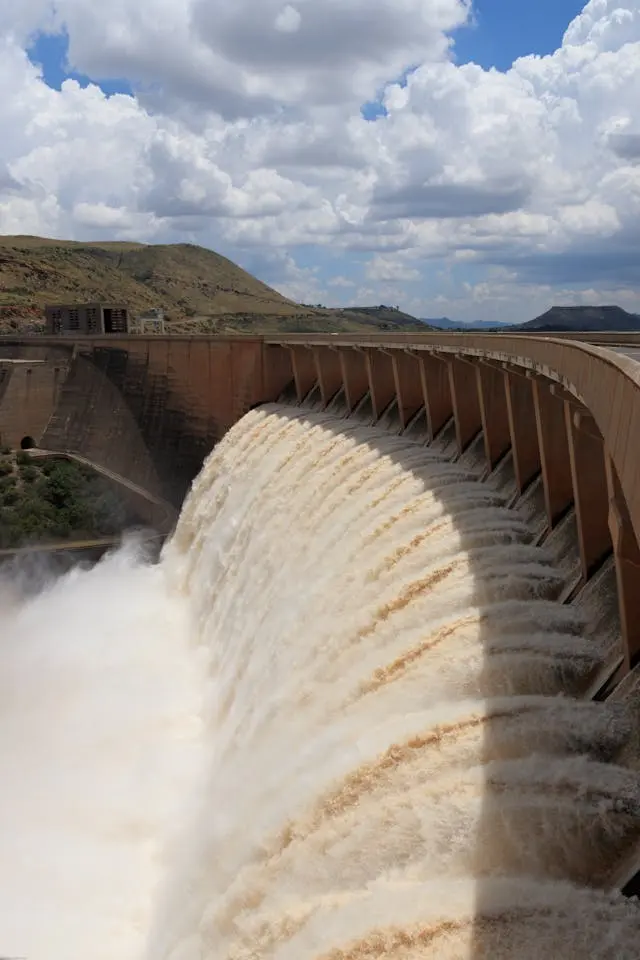

9. Conclusion
Mangla Dam remains one of the most important infrastructure projects in Pakistan’s history, serving multiple purposes that benefit millions of people across the country. From providing essential water for irrigation to generating clean electricity and controlling floods, the dam plays a crucial role in the nation’s economic and environmental stability. As Pakistan continues to face challenges related to water management and energy production, Mangla Dam will remain a vital asset for the country’s growth and development.